Integral of 2xe^(x^2) dx
The solution
You have entered
[src]
1 / | | / 2\ | \x / | 2*x*e dx | / 0
$$\int\limits_{0}^{1} 2 x e^{x^{2}}\, dx$$
Detail solution
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
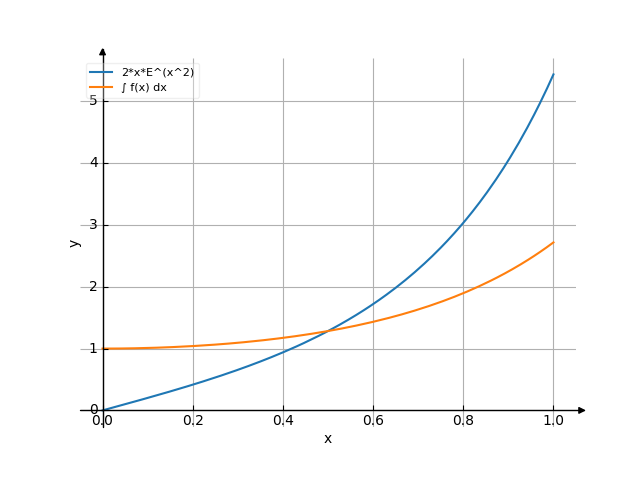
The graph
The graph
Use the examples entering the upper and lower limits of integration.

![Find the integral of y = f(x) = 2xe^(x²) dx (2xe to the power of (x squared)) - with detailed solution [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] 2xe^(x^2)](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/indefinite/2/f4/01da41afb16341879bd0dcfb64915.png)
 Integral of 2xe^(x^2)
Integral of 2xe^(x^2)
 Integral of cos^5(2x)
Integral of cos^5(2x)
 Integral of 4cosx
Integral of 4cosx
 Integral of cos^3x/sin^4x
Integral of cos^3x/sin^4x
 2xe^(x^2)
2xe^(x^2)