Graphing y = sqrt(x^2)
The solution
The graph of the function
The points of intersection with the X-axis coordinate
Graph of the function intersects the axis X at f = 0
so we need to solve the equation:
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
so we need to solve the equation:
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Extrema of the function
In order to find the extrema, we need to solve the equation
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
Inflection points
Let's find the inflection points, we'll need to solve the equation for this
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{\operatorname{sign}{\left(x \right)} - \frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}}{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 66$$
$$x_{2} = 94$$
$$x_{3} = 98$$
$$x_{4} = 46$$
$$x_{5} = 24$$
$$x_{6} = -24$$
$$x_{7} = -46$$
$$x_{8} = 18$$
$$x_{9} = 22$$
$$x_{10} = -82$$
$$x_{11} = -74$$
$$x_{12} = -42$$
$$x_{13} = 50$$
$$x_{14} = 64$$
$$x_{15} = 36$$
$$x_{16} = -60$$
$$x_{17} = -66$$
$$x_{18} = -8$$
$$x_{19} = -26$$
$$x_{20} = -2$$
$$x_{21} = 86$$
$$x_{22} = 42$$
$$x_{23} = -36$$
$$x_{24} = 100$$
$$x_{25} = -18$$
$$x_{26} = 12$$
$$x_{27} = 90$$
$$x_{28} = -88$$
$$x_{29} = -92$$
$$x_{30} = 52$$
$$x_{31} = -44$$
$$x_{32} = 6$$
$$x_{33} = 38$$
$$x_{34} = 96$$
$$x_{35} = -84$$
$$x_{36} = 10$$
$$x_{37} = -98$$
$$x_{38} = 62$$
$$x_{39} = -28$$
$$x_{40} = 14$$
$$x_{41} = 30$$
$$x_{42} = -14$$
$$x_{43} = -72$$
$$x_{44} = -20$$
$$x_{45} = 54$$
$$x_{46} = -52$$
$$x_{47} = -12$$
$$x_{48} = 68$$
$$x_{49} = 32$$
$$x_{50} = 28$$
$$x_{51} = -16$$
$$x_{52} = -40$$
$$x_{53} = -48$$
$$x_{54} = 44$$
$$x_{55} = -6$$
$$x_{56} = -50$$
$$x_{57} = 16$$
$$x_{58} = -78$$
$$x_{59} = 4$$
$$x_{60} = -56$$
$$x_{61} = -10$$
$$x_{62} = 74$$
$$x_{63} = -34$$
$$x_{64} = -62$$
$$x_{65} = -58$$
$$x_{66} = 84$$
$$x_{67} = -68$$
$$x_{68} = 76$$
$$x_{69} = -94$$
$$x_{70} = -86$$
$$x_{71} = -4$$
$$x_{72} = 40$$
$$x_{73} = -96$$
$$x_{74} = -70$$
$$x_{75} = 8$$
$$x_{76} = 82$$
$$x_{77} = -80$$
$$x_{78} = -76$$
$$x_{79} = -38$$
$$x_{80} = -32$$
$$x_{81} = -30$$
$$x_{82} = -54$$
$$x_{83} = 48$$
$$x_{84} = 20$$
$$x_{85} = 56$$
$$x_{86} = 58$$
$$x_{87} = 78$$
$$x_{88} = 70$$
$$x_{89} = 60$$
$$x_{90} = 92$$
$$x_{91} = -90$$
$$x_{92} = 72$$
$$x_{93} = 88$$
$$x_{94} = 2$$
$$x_{95} = -64$$
$$x_{96} = -100$$
$$x_{97} = 80$$
$$x_{98} = -22$$
$$x_{99} = 34$$
$$x_{100} = 26$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[-30, 30\right]$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -30\right] \cup \left[30, \infty\right)$$
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{\operatorname{sign}{\left(x \right)} - \frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}}{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 66$$
$$x_{2} = 94$$
$$x_{3} = 98$$
$$x_{4} = 46$$
$$x_{5} = 24$$
$$x_{6} = -24$$
$$x_{7} = -46$$
$$x_{8} = 18$$
$$x_{9} = 22$$
$$x_{10} = -82$$
$$x_{11} = -74$$
$$x_{12} = -42$$
$$x_{13} = 50$$
$$x_{14} = 64$$
$$x_{15} = 36$$
$$x_{16} = -60$$
$$x_{17} = -66$$
$$x_{18} = -8$$
$$x_{19} = -26$$
$$x_{20} = -2$$
$$x_{21} = 86$$
$$x_{22} = 42$$
$$x_{23} = -36$$
$$x_{24} = 100$$
$$x_{25} = -18$$
$$x_{26} = 12$$
$$x_{27} = 90$$
$$x_{28} = -88$$
$$x_{29} = -92$$
$$x_{30} = 52$$
$$x_{31} = -44$$
$$x_{32} = 6$$
$$x_{33} = 38$$
$$x_{34} = 96$$
$$x_{35} = -84$$
$$x_{36} = 10$$
$$x_{37} = -98$$
$$x_{38} = 62$$
$$x_{39} = -28$$
$$x_{40} = 14$$
$$x_{41} = 30$$
$$x_{42} = -14$$
$$x_{43} = -72$$
$$x_{44} = -20$$
$$x_{45} = 54$$
$$x_{46} = -52$$
$$x_{47} = -12$$
$$x_{48} = 68$$
$$x_{49} = 32$$
$$x_{50} = 28$$
$$x_{51} = -16$$
$$x_{52} = -40$$
$$x_{53} = -48$$
$$x_{54} = 44$$
$$x_{55} = -6$$
$$x_{56} = -50$$
$$x_{57} = 16$$
$$x_{58} = -78$$
$$x_{59} = 4$$
$$x_{60} = -56$$
$$x_{61} = -10$$
$$x_{62} = 74$$
$$x_{63} = -34$$
$$x_{64} = -62$$
$$x_{65} = -58$$
$$x_{66} = 84$$
$$x_{67} = -68$$
$$x_{68} = 76$$
$$x_{69} = -94$$
$$x_{70} = -86$$
$$x_{71} = -4$$
$$x_{72} = 40$$
$$x_{73} = -96$$
$$x_{74} = -70$$
$$x_{75} = 8$$
$$x_{76} = 82$$
$$x_{77} = -80$$
$$x_{78} = -76$$
$$x_{79} = -38$$
$$x_{80} = -32$$
$$x_{81} = -30$$
$$x_{82} = -54$$
$$x_{83} = 48$$
$$x_{84} = 20$$
$$x_{85} = 56$$
$$x_{86} = 58$$
$$x_{87} = 78$$
$$x_{88} = 70$$
$$x_{89} = 60$$
$$x_{90} = 92$$
$$x_{91} = -90$$
$$x_{92} = 72$$
$$x_{93} = 88$$
$$x_{94} = 2$$
$$x_{95} = -64$$
$$x_{96} = -100$$
$$x_{97} = 80$$
$$x_{98} = -22$$
$$x_{99} = 34$$
$$x_{100} = 26$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[-30, 30\right]$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -30\right] \cup \left[30, \infty\right)$$
Horizontal asymptotes
Let’s find horizontal asymptotes with help of the limits of this function at x->+oo and x->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty} \sqrt{x^{2}} = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the left doesn’t exist
$$\lim_{x \to \infty} \sqrt{x^{2}} = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty} \sqrt{x^{2}} = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the left doesn’t exist
$$\lim_{x \to \infty} \sqrt{x^{2}} = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
Inclined asymptotes
Inclined asymptote can be found by calculating the limit of sqrt(x^2), divided by x at x->+oo and x ->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}\right) = -1$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the left:
$$y = - x$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}\right) = 1$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the right:
$$y = x$$
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}\right) = -1$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the left:
$$y = - x$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\left|{x}\right|}{x}\right) = 1$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the right:
$$y = x$$
Even and odd functions
Let's check, whether the function even or odd by using relations f = f(-x) и f = -f(-x).
So, check:
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = \sqrt{x^{2}}$$
- Yes
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = - \sqrt{x^{2}}$$
- No
so, the function
is
even
So, check:
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = \sqrt{x^{2}}$$
- Yes
$$\sqrt{x^{2}} = - \sqrt{x^{2}}$$
- No
so, the function
is
even

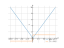 sqrt(x^2)
sqrt(x^2)
 sqrt(x^2)
sqrt(x^2)
 sqrt(x^2)
sqrt(x^2)