sqrt(118-39x)=8-3x equation
The teacher will be very surprised to see your correct solution 😉
The solution
Detail solution
Given the equation
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
We raise the equation sides to 2-th degree
$$- 39 x + 118 = \left(- 3 x + 8\right)^{2}$$
$$- 39 x + 118 = 9 x^{2} - 48 x + 64$$
Transfer the right side of the equation left part with negative sign
$$- 9 x^{2} + 9 x + 54 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
$$a\ x^2 + b\ x + c = 0$$
A quadratic equation can be solved using the discriminant
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where $D = b^2 - 4 a c$ is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = -9$$
$$b = 9$$
$$c = 54$$
, then
$$D = b^2 - 4\ a\ c = $$
$$9^{2} - \left(-9\right) 4 \cdot 54 = 2025$$
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
$$x_1 = \frac{(-b + \sqrt{D})}{2 a}$$
$$x_2 = \frac{(-b - \sqrt{D})}{2 a}$$
or
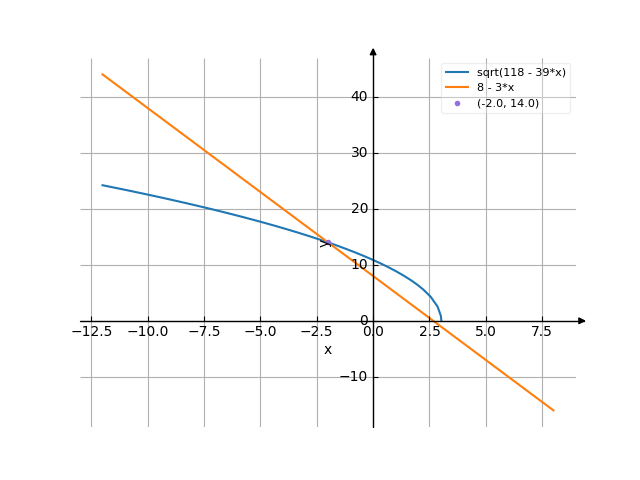
$$x_{1} = -2$$
Simplify
$$x_{2} = 3$$
Simplify
Because
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
and
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} \geq 0$$
then
$$- 3 x + 8 >= 0$$
or
$$x \leq \frac{8}{3}$$
$$-\infty < x$$
The final answer:
$$x_{1} = -2$$
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
We raise the equation sides to 2-th degree
$$- 39 x + 118 = \left(- 3 x + 8\right)^{2}$$
$$- 39 x + 118 = 9 x^{2} - 48 x + 64$$
Transfer the right side of the equation left part with negative sign
$$- 9 x^{2} + 9 x + 54 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
$$a\ x^2 + b\ x + c = 0$$
A quadratic equation can be solved using the discriminant
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where $D = b^2 - 4 a c$ is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = -9$$
$$b = 9$$
$$c = 54$$
, then
$$D = b^2 - 4\ a\ c = $$
$$9^{2} - \left(-9\right) 4 \cdot 54 = 2025$$
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
$$x_1 = \frac{(-b + \sqrt{D})}{2 a}$$
$$x_2 = \frac{(-b - \sqrt{D})}{2 a}$$
or
$$x_{1} = -2$$
Simplify
$$x_{2} = 3$$
Simplify
Because
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} = - 3 x + 8$$
and
$$\sqrt{- 39 x + 118} \geq 0$$
then
$$- 3 x + 8 >= 0$$
or
$$x \leq \frac{8}{3}$$
$$-\infty < x$$
The final answer:
$$x_{1} = -2$$
Sum and product of roots
[src]
sum
-2
$$\left(-2\right)$$
=
-2
$$-2$$
product
-2
$$\left(-2\right)$$
=
-2
$$-2$$
The graph

![Solve the equation sqrt(118-39x)=8-3x (square root of (118 minus 39x) equally 8 minus 3x) - Find the roots of the equation in detail step by step. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] sqrt(118-39x)=8-3x](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/equation/4/a6/d47c6626213b46c56d70aef30322e.png)
 Equation sqrt(118-39x)=8-3x
Equation sqrt(118-39x)=8-3x
 Equation а²+6а+9+(а+3)(3-а)
Equation а²+6а+9+(а+3)(3-а)