Integral exp(2x)*sin(3x) dx
A solução
You have entered
[src]
1 / | | 2*x | e *sin(3*x) dx | / 0
$$\int\limits_{0}^{1} e^{2 x} \sin{\left(3 x \right)}\, dx$$
Integral(exp(2*x)*sin(3*x), (x, 0, 1))
Detail solution
-
Use integration by parts, noting that the integrand eventually repeats itself.
-
For the integrand :
Let and let .
Then .
-
For the integrand :
Let and let .
Then .
-
Notice that the integrand has repeated itself, so move it to one side:
Therefore,
-
-
Now simplify:
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
The answer (Indefinite)
[src]
/ | 2*x 2*x | 2*x 3*cos(3*x)*e 2*e *sin(3*x) | e *sin(3*x) dx = C - --------------- + --------------- | 13 13 /
$${{e^{2\,x}\,\left(2\,\sin \left(3\,x\right)-3\,\cos \left(3\,x
\right)\right)}\over{13}}$$
The answer
[src]
2 2 3 3*cos(3)*e 2*e *sin(3) -- - ----------- + ----------- 13 13 13
$${{2\,e^2\,\sin 3-3\,e^2\,\cos 3}\over{13}}+{{3}\over{13}}$$
=
=
2 2 3 3*cos(3)*e 2*e *sin(3) -- - ----------- + ----------- 13 13 13
$$\frac{2 e^{2} \sin{\left(3 \right)}}{13} + \frac{3}{13} - \frac{3 e^{2} \cos{\left(3 \right)}}{13}$$
Gráfico
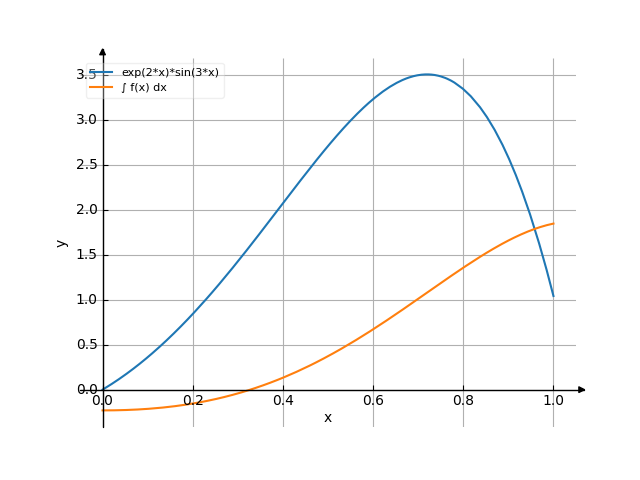
Estes exemplos também podem ser usados ao introduzir os limites superior e inferior de integração.

![Encontrar o integral de y = f(x) = exp(2x)*sin(3x) dx (exponencial de (2x) multiplicar por seno de (3x)) - com solução detalhada [HÁ RESPOSTA!] exp(2x)*sin(3x)](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/indefinite/4/d0/8f5a5f4404d40a361271eb328a509.png)
 Integral 1/(xlog(x))
Integral 1/(xlog(x))
 Integral exp(2x)*sin(3x)
Integral exp(2x)*sin(3x)
 Integral 7x^2-3x+5
Integral 7x^2-3x+5