Graphing y = (x+2)*e^x
The solution
You have entered
[src]
x f(x) = (x + 2)*E
$$f{\left(x \right)} = e^{x} \left(x + 2\right)$$
f = E^x*(x + 2)
The graph of the function
The points of intersection with the X-axis coordinate
Graph of the function intersects the axis X at f = 0
so we need to solve the equation:
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = -2$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = -99.1205993527235$$
$$x_{2} = -45.5740005056864$$
$$x_{3} = -111.089608132217$$
$$x_{4} = -95.1329980618501$$
$$x_{5} = -101.114833112977$$
$$x_{6} = -35.9540517145623$$
$$x_{7} = -113.085180982879$$
$$x_{8} = -47.5287883412543$$
$$x_{9} = -117.076847342498$$
$$x_{10} = -79.1981473783759$$
$$x_{11} = -115.080930865701$$
$$x_{12} = -59.3470343910748$$
$$x_{13} = -119.072920781941$$
$$x_{14} = -32.2742313644863$$
$$x_{15} = -107.099039845199$$
$$x_{16} = -69.2586229734047$$
$$x_{17} = -71.2447823410302$$
$$x_{18} = -73.2319064024203$$
$$x_{19} = -41.6870583075465$$
$$x_{20} = -89.1541152286569$$
$$x_{21} = -37.8463765939876$$
$$x_{22} = -85.1702113647074$$
$$x_{23} = -53.4230249783974$$
$$x_{24} = -83.1789726997072$$
$$x_{25} = -105.10407015753$$
$$x_{26} = -97.1266472537626$$
$$x_{27} = -51.4541901054407$$
$$x_{28} = -109.094223645316$$
$$x_{29} = -93.1396752246407$$
$$x_{30} = -87.1619388762717$$
$$x_{31} = -65.2896724119287$$
$$x_{32} = -34.0913241206348$$
$$x_{33} = -43.6261544568938$$
$$x_{34} = -63.3071694941258$$
$$x_{35} = -103.109329237227$$
$$x_{36} = -49.4891864944529$$
$$x_{37} = -39.7592416454249$$
$$x_{38} = -81.1882678183563$$
$$x_{39} = -91.146704685936$$
$$x_{40} = -67.2735421114241$$
$$x_{41} = -121.06914228288$$
$$x_{42} = -61.3262172000187$$
$$x_{43} = -55.3950840173982$$
$$x_{44} = -57.369883839131$$
$$x_{45} = -75.2198969347223$$
$$x_{46} = -2$$
$$x_{47} = -77.2086687051389$$
so we need to solve the equation:
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = -2$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = -99.1205993527235$$
$$x_{2} = -45.5740005056864$$
$$x_{3} = -111.089608132217$$
$$x_{4} = -95.1329980618501$$
$$x_{5} = -101.114833112977$$
$$x_{6} = -35.9540517145623$$
$$x_{7} = -113.085180982879$$
$$x_{8} = -47.5287883412543$$
$$x_{9} = -117.076847342498$$
$$x_{10} = -79.1981473783759$$
$$x_{11} = -115.080930865701$$
$$x_{12} = -59.3470343910748$$
$$x_{13} = -119.072920781941$$
$$x_{14} = -32.2742313644863$$
$$x_{15} = -107.099039845199$$
$$x_{16} = -69.2586229734047$$
$$x_{17} = -71.2447823410302$$
$$x_{18} = -73.2319064024203$$
$$x_{19} = -41.6870583075465$$
$$x_{20} = -89.1541152286569$$
$$x_{21} = -37.8463765939876$$
$$x_{22} = -85.1702113647074$$
$$x_{23} = -53.4230249783974$$
$$x_{24} = -83.1789726997072$$
$$x_{25} = -105.10407015753$$
$$x_{26} = -97.1266472537626$$
$$x_{27} = -51.4541901054407$$
$$x_{28} = -109.094223645316$$
$$x_{29} = -93.1396752246407$$
$$x_{30} = -87.1619388762717$$
$$x_{31} = -65.2896724119287$$
$$x_{32} = -34.0913241206348$$
$$x_{33} = -43.6261544568938$$
$$x_{34} = -63.3071694941258$$
$$x_{35} = -103.109329237227$$
$$x_{36} = -49.4891864944529$$
$$x_{37} = -39.7592416454249$$
$$x_{38} = -81.1882678183563$$
$$x_{39} = -91.146704685936$$
$$x_{40} = -67.2735421114241$$
$$x_{41} = -121.06914228288$$
$$x_{42} = -61.3262172000187$$
$$x_{43} = -55.3950840173982$$
$$x_{44} = -57.369883839131$$
$$x_{45} = -75.2198969347223$$
$$x_{46} = -2$$
$$x_{47} = -77.2086687051389$$
Extrema of the function
In order to find the extrema, we need to solve the equation
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$e^{x} + \left(x + 2\right) e^{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = -3$$
The values of the extrema at the points:
Intervals of increase and decrease of the function:
Let's find intervals where the function increases and decreases, as well as minima and maxima of the function, for this let's look how the function behaves itself in the extremas and at the slightest deviation from:
Minima of the function at points:
$$x_{1} = -3$$
The function has no maxima
Decreasing at intervals
$$\left[-3, \infty\right)$$
Increasing at intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -3\right]$$
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$e^{x} + \left(x + 2\right) e^{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = -3$$
The values of the extrema at the points:
-3 (-3, -e )
Intervals of increase and decrease of the function:
Let's find intervals where the function increases and decreases, as well as minima and maxima of the function, for this let's look how the function behaves itself in the extremas and at the slightest deviation from:
Minima of the function at points:
$$x_{1} = -3$$
The function has no maxima
Decreasing at intervals
$$\left[-3, \infty\right)$$
Increasing at intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -3\right]$$
Inflection points
Let's find the inflection points, we'll need to solve the equation for this
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\left(x + 4\right) e^{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = -4$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[-4, \infty\right)$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -4\right]$$
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\left(x + 4\right) e^{x} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = -4$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[-4, \infty\right)$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, -4\right]$$
Horizontal asymptotes
Let’s find horizontal asymptotes with help of the limits of this function at x->+oo and x->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(e^{x} \left(x + 2\right)\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = 0$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(e^{x} \left(x + 2\right)\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(e^{x} \left(x + 2\right)\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = 0$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(e^{x} \left(x + 2\right)\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
horizontal asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
Inclined asymptotes
Inclined asymptote can be found by calculating the limit of (x + 2)*E^x, divided by x at x->+oo and x ->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\left(x + 2\right) e^{x}}{x}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the right
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\left(x + 2\right) e^{x}}{x}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\left(x + 2\right) e^{x}}{x}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the right
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\left(x + 2\right) e^{x}}{x}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote on the right doesn’t exist
Even and odd functions
Let's check, whether the function even or odd by using relations f = f(-x) и f = -f(-x).
So, check:
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = \left(2 - x\right) e^{- x}$$
- No
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = - \left(2 - x\right) e^{- x}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd
So, check:
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = \left(2 - x\right) e^{- x}$$
- No
$$e^{x} \left(x + 2\right) = - \left(2 - x\right) e^{- x}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd

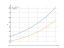 (x+2)*e^x
(x+2)*e^x