Graphing y = tan(x/2)
The solution
You have entered
[src]
/x\
f(x) = tan|-|
\2/
$$f{\left(x \right)} = \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}$$
f = tan(x/2)
The graph of the function
The points of intersection with the X-axis coordinate
Graph of the function intersects the axis X at f = 0
so we need to solve the equation:
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = 94.2477796076938$$
$$x_{2} = -37.6991118430775$$
$$x_{3} = -31.4159265358979$$
$$x_{4} = -81.6814089933346$$
$$x_{5} = 6.28318530717959$$
$$x_{6} = 62.8318530717959$$
$$x_{7} = 81.6814089933346$$
$$x_{8} = 100.530964914873$$
$$x_{9} = 50.2654824574367$$
$$x_{10} = -56.5486677646163$$
$$x_{11} = 25.1327412287183$$
$$x_{12} = -87.9645943005142$$
$$x_{13} = -6.28318530717959$$
$$x_{14} = 12.5663706143592$$
$$x_{15} = 75.398223686155$$
$$x_{16} = 56.5486677646163$$
$$x_{17} = -12.5663706143592$$
$$x_{18} = 18.8495559215388$$
$$x_{19} = -94.2477796076938$$
$$x_{20} = -25.1327412287183$$
$$x_{21} = -75.398223686155$$
$$x_{22} = 31.4159265358979$$
$$x_{23} = 43.9822971502571$$
$$x_{24} = -50.2654824574367$$
$$x_{25} = -43.9822971502571$$
$$x_{26} = 69.1150383789755$$
$$x_{27} = -18.8495559215388$$
$$x_{28} = 0$$
$$x_{29} = -62.8318530717959$$
$$x_{30} = 87.9645943005142$$
$$x_{31} = 37.6991118430775$$
$$x_{32} = -100.530964914873$$
$$x_{33} = -69.1150383789755$$
so we need to solve the equation:
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = 94.2477796076938$$
$$x_{2} = -37.6991118430775$$
$$x_{3} = -31.4159265358979$$
$$x_{4} = -81.6814089933346$$
$$x_{5} = 6.28318530717959$$
$$x_{6} = 62.8318530717959$$
$$x_{7} = 81.6814089933346$$
$$x_{8} = 100.530964914873$$
$$x_{9} = 50.2654824574367$$
$$x_{10} = -56.5486677646163$$
$$x_{11} = 25.1327412287183$$
$$x_{12} = -87.9645943005142$$
$$x_{13} = -6.28318530717959$$
$$x_{14} = 12.5663706143592$$
$$x_{15} = 75.398223686155$$
$$x_{16} = 56.5486677646163$$
$$x_{17} = -12.5663706143592$$
$$x_{18} = 18.8495559215388$$
$$x_{19} = -94.2477796076938$$
$$x_{20} = -25.1327412287183$$
$$x_{21} = -75.398223686155$$
$$x_{22} = 31.4159265358979$$
$$x_{23} = 43.9822971502571$$
$$x_{24} = -50.2654824574367$$
$$x_{25} = -43.9822971502571$$
$$x_{26} = 69.1150383789755$$
$$x_{27} = -18.8495559215388$$
$$x_{28} = 0$$
$$x_{29} = -62.8318530717959$$
$$x_{30} = 87.9645943005142$$
$$x_{31} = 37.6991118430775$$
$$x_{32} = -100.530964914873$$
$$x_{33} = -69.1150383789755$$
Extrema of the function
In order to find the extrema, we need to solve the equation
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{\tan^{2}{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{2} + \frac{1}{2} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{\tan^{2}{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{2} + \frac{1}{2} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
Inflection points
Let's find the inflection points, we'll need to solve the equation for this
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{\left(\tan^{2}{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} + 1\right) \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{2} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[0, \infty\right)$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, 0\right]$$
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{\left(\tan^{2}{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} + 1\right) \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{2} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left[0, \infty\right)$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, 0\right]$$
Horizontal asymptotes
Let’s find horizontal asymptotes with help of the limits of this function at x->+oo and x->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty} \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty} \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the right:
$$y = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty} \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty} \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the right:
$$y = \left\langle -\infty, \infty\right\rangle$$
Inclined asymptotes
Inclined asymptote can be found by calculating the limit of tan(x/2), divided by x at x->+oo and x ->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right) = \lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the left:
$$y = x \lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right) = \lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the right:
$$y = x \lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right) = \lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the left:
$$y = x \lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right) = \lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined asymptote equation on the right:
$$y = x \lim_{x \to \infty}\left(\frac{\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}}{x}\right)$$
Even and odd functions
Let's check, whether the function even or odd by using relations f = f(-x) и f = -f(-x).
So, check:
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}$$
- No
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd
So, check:
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}$$
- No
$$\tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = \tan{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd
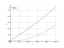
The graph


![The graph y = f(x) = tan(x/2) (tangent of (x divide by 2)) - plot the function graph and draw it. Curve sketching this function. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] tan(x/2)](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/xy/c/45/fc44a2e95bb970fc47ee5c5c1f12e.png)
 |x^2-x-2|
|x^2-x-2|
 tan(x/2)
tan(x/2)
 tan(x/2)
tan(x/2)
 tan(x/2)
tan(x/2)