Sum of series arcsin(n+1/n^2)
The solution
You have entered
[src]
oo ____ \ ` \ / 1 \ \ asin|n + --| / | 2| / \ n / /___, n = 1
$$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
Sum(asin(n + 1/(n^2)), (n, 1, oo))
The radius of convergence of the power series
Given number:
$$\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
It is a series of species
$$a_{n} \left(c x - x_{0}\right)^{d n}$$
- power series.
The radius of convergence of a power series can be calculated by the formula:
$$R^{d} = \frac{x_{0} + \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{a_{n}}{a_{n + 1}}}\right|}{c}$$
In this case
$$a_{n} = \operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
and
$$x_{0} = 0$$
,
$$d = 0$$
,
$$c = 1$$
then
$$1 = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}}{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + 1 + \frac{1}{\left(n + 1\right)^{2}} \right)}}}\right|$$
Let's take the limit
we find
$$1 = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}}{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + 1 + \frac{1}{\left(n + 1\right)^{2}} \right)}}}\right|$$
$$\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
It is a series of species
$$a_{n} \left(c x - x_{0}\right)^{d n}$$
- power series.
The radius of convergence of a power series can be calculated by the formula:
$$R^{d} = \frac{x_{0} + \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{a_{n}}{a_{n + 1}}}\right|}{c}$$
In this case
$$a_{n} = \operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
and
$$x_{0} = 0$$
,
$$d = 0$$
,
$$c = 1$$
then
$$1 = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}}{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + 1 + \frac{1}{\left(n + 1\right)^{2}} \right)}}}\right|$$
Let's take the limit
we find
$$1 = \lim_{n \to \infty} \left|{\frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}}{\operatorname{asin}{\left(n + 1 + \frac{1}{\left(n + 1\right)^{2}} \right)}}}\right|$$
False
The answer
[src]
oo ____ \ ` \ / 1 \ \ asin|n + --| / | 2| / \ n / /___, n = 1
$$\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \operatorname{asin}{\left(n + \frac{1}{n^{2}} \right)}$$
Sum(asin(n + n^(-2)), (n, 1, oo))
Examples of finding the sum of a series
- The Sum of the Power Series
x^n/n
(x-1)^n
- Factorial
1/2^(n!)
n^2/n!
x^n/n!
k!/(n!*(n+k)!)
- Flint Hills Series
csc(n)^2/n^3
- Basel problem
1/n^2
1/n^4
1/n^6
- Harmonic series
1/n
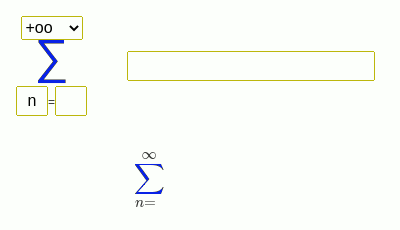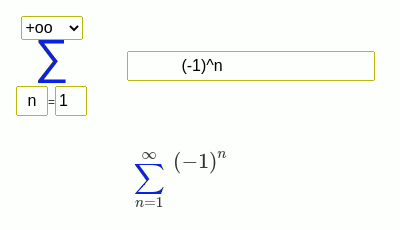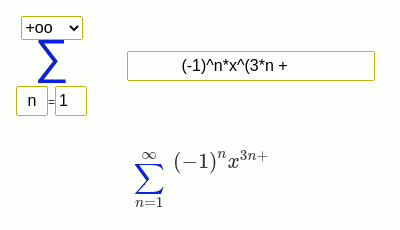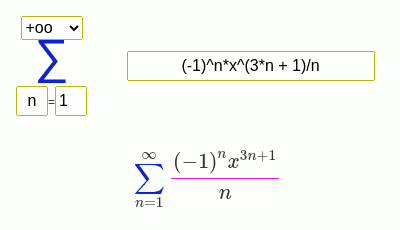
- Grandi's series
(-1)^n
- Alternating series
(-1)^(n + 1)/n
(n + 2)*(-1)^(n - 1)
(3*n - 1)/(-5)^n
(-1)^(n - 1)*n/(6*n - 5)
- Newton–Mercator series
(-1)^(n + 1)/n*x^n
- Exam the series for convergence
(3*n - 1)/(-5)^n

 3^(n-1)/8^(n-1)
3^(n-1)/8^(n-1)
 arctan(n)/(n!)^2
arctan(n)/(n!)^2
 (n+sqrt(n))/(2n^2+n-1)
(n+sqrt(n))/(2n^2+n-1)
 (1000!)/(n!*(1000-n)!)*((0.025)^n)*((1-0.025)^(1000-n))
(1000!)/(n!*(1000-n)!)*((0.025)^n)*((1-0.025)^(1000-n))