Integral of -0,1/e^xdx dx
The solution
You have entered
[src]
11/5 / | | 1 | -1/10*--*1 dx | x | e | / 2/5
$$\int\limits_{\frac{2}{5}}^{\frac{11}{5}} \left(\left(- \frac{1}{10}\right) \frac{1}{e^{x}} 1\right)\, dx$$
Integral(-1/10*1/E^x, (x, 2/5, 11/5))
Detail solution
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of is when :
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
The answer (Indefinite)
[src]
/ | -x | 1 e | -1/10*--*1 dx = C + --- | x 10 | e | /
$${{e^ {- x }}\over{10}}$$
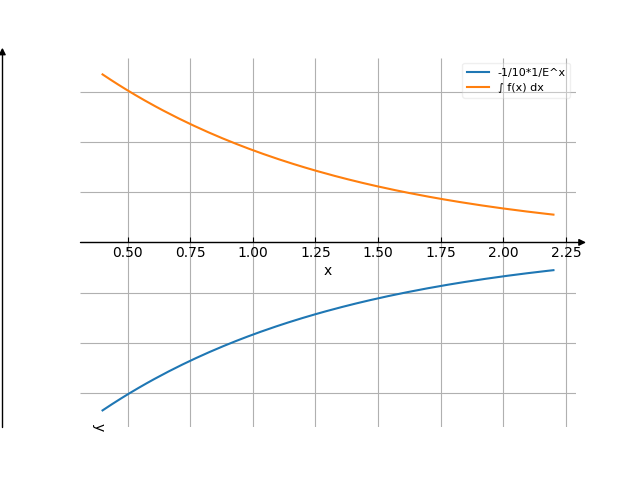
The graph
The answer
[src]
-2/5 -11/5
e e
- ----- + ------
10 10
$$-{{e^ {- {{2}\over{5}} }-e^ {- {{11}\over{5}} }}\over{10}}$$
=
=
-2/5 -11/5
e e
- ----- + ------
10 10
$$- \frac{1}{10 e^{\frac{2}{5}}} + \frac{1}{10 e^{\frac{11}{5}}}$$
The graph
Use the examples entering the upper and lower limits of integration.

![Find the integral of y = f(x) = -0,1/e^xdx (minus 0,1 divide by e to the power of xdx) - with detailed solution [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] -0,1/e^xdx](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/indefinite/a/35/828f4daf68992ad7dd46b14c30c22.png)
 Integral of sin²xcos²x
Integral of sin²xcos²x
 Integral of tg2x
Integral of tg2x
 Integral of 1/(x^2-9)
Integral of 1/(x^2-9)