x^2+3x>10 inequation
The solution
Detail solution
Given the inequality:
$$x^{2} + 3 x > 10$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$x^{2} + 3 x = 10$$
Solve:
Move right part of the equation to
left part with negative sign.
The equation is transformed from
$$x^{2} + 3 x = 10$$
to
$$\left(x^{2} + 3 x\right) - 10 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 3$$
$$c = -10$$
, then
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
or
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
This roots
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$x_{0} < x_{2}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$x_{0} = x_{2} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$-5 + - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$- \frac{51}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$x^{2} + 3 x > 10$$
$$\frac{\left(-51\right) 3}{10} + \left(- \frac{51}{10}\right)^{2} > 10$$
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$x < -5$$
Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$x < -5$$
$$x > 2$$
$$x^{2} + 3 x > 10$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$x^{2} + 3 x = 10$$
Solve:
Move right part of the equation to
left part with negative sign.
The equation is transformed from
$$x^{2} + 3 x = 10$$
to
$$\left(x^{2} + 3 x\right) - 10 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
a*x^2 + b*x + c = 0
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 3$$
$$c = -10$$
, then
D = b^2 - 4 * a * c =
(3)^2 - 4 * (1) * (-10) = 49
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
x1 = (-b + sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
x2 = (-b - sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
or
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
$$x_{2} = -5$$
This roots
$$x_{2} = -5$$
$$x_{1} = 2$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$x_{0} < x_{2}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$x_{0} = x_{2} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$-5 + - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$- \frac{51}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$x^{2} + 3 x > 10$$
$$\frac{\left(-51\right) 3}{10} + \left(- \frac{51}{10}\right)^{2} > 10$$
1071 ---- > 10 100
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$x < -5$$
_____ _____
\ /
-------ο-------ο-------
x2 x1Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$x < -5$$
$$x > 2$$
Solving inequality on a graph
Rapid solution 2
[src]
(-oo, -5) U (2, oo)
$$x\ in\ \left(-\infty, -5\right) \cup \left(2, \infty\right)$$
x in Union(Interval.open(-oo, -5), Interval.open(2, oo))
Rapid solution
[src]
Or(And(-oo < x, x < -5), And(2 < x, x < oo))
$$\left(-\infty < x \wedge x < -5\right) \vee \left(2 < x \wedge x < \infty\right)$$
((-oo < x)∧(x < -5))∨((2 < x)∧(x < oo))

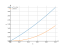 x^2+3x
x^2+3x
 10
10
 x^2+3x
x^2+3x
 10
10
 10
10