|z|>2 inequation
The solution
Detail solution
Given the inequality:
$$\left|{z}\right| > 2$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$\left|{z}\right| = 2$$
Solve:
For every modulo expressions in the equation
allow cases, when this expressions ">=0" or "<0",
solve the resulting equation.
1.
$$z \geq 0$$
or
$$0 \leq z \wedge z < \infty$$
we get the equation
$$z - 2 = 0$$
after simplifying we get
$$z - 2 = 0$$
the solution in this interval:
$$z_{1} = 2$$
2.
$$z < 0$$
or
$$-\infty < z \wedge z < 0$$
we get the equation
$$- z - 2 = 0$$
after simplifying we get
$$- z - 2 = 0$$
the solution in this interval:
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
$$z_{2} = -2$$
This roots
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$z_{0} < z_{2}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$z_{0} = z_{2} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$-2 + - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$- \frac{21}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$\left|{z}\right| > 2$$
$$\left|{- \frac{21}{10}}\right| > 2$$
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$z < -2$$
Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$z < -2$$
$$z > 2$$
$$\left|{z}\right| > 2$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$\left|{z}\right| = 2$$
Solve:
For every modulo expressions in the equation
allow cases, when this expressions ">=0" or "<0",
solve the resulting equation.
1.
$$z \geq 0$$
or
$$0 \leq z \wedge z < \infty$$
we get the equation
$$z - 2 = 0$$
after simplifying we get
$$z - 2 = 0$$
the solution in this interval:
$$z_{1} = 2$$
2.
$$z < 0$$
or
$$-\infty < z \wedge z < 0$$
we get the equation
$$- z - 2 = 0$$
after simplifying we get
$$- z - 2 = 0$$
the solution in this interval:
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
$$z_{2} = -2$$
This roots
$$z_{2} = -2$$
$$z_{1} = 2$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$z_{0} < z_{2}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$z_{0} = z_{2} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$-2 + - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$- \frac{21}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$\left|{z}\right| > 2$$
$$\left|{- \frac{21}{10}}\right| > 2$$
21 -- > 2 10
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$z < -2$$
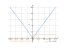
_____ _____
\ /
-------ο-------ο-------
z2 z1Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$z < -2$$
$$z > 2$$
Solving inequality on a graph
Rapid solution 2
[src]
(-oo, -2) U (2, oo)
$$z\ in\ \left(-\infty, -2\right) \cup \left(2, \infty\right)$$
z in Union(Interval.open(-oo, -2), Interval.open(2, oo))
Rapid solution
[src]
Or(And(-oo < z, z < -2), And(2 < z, z < oo))
$$\left(-\infty < z \wedge z < -2\right) \vee \left(2 < z \wedge z < \infty\right)$$
((-oo < z)∧(z < -2))∨((2 < z)∧(z < oo))

 |z|
|z|