Graphing y = -2x/(x^2-1)^2
The solution
You have entered
[src]
-2*x
f(x) = ---------
2
/ 2 \
\x - 1/
$$f{\left(x \right)} = - \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}$$
f = -2*x/((x^2 - 1*1)^2)
The graph of the function
The domain of the function
The points at which the function is not precisely defined:
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
The points of intersection with the X-axis coordinate
Graph of the function intersects the axis X at f = 0
so we need to solve the equation:
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = -12637.7892988554$$
$$x_{2} = -29595.9777734643$$
$$x_{3} = 27183.9940576599$$
$$x_{4} = -25357.1956280906$$
$$x_{5} = 39051.9598251782$$
$$x_{6} = 31422.6838625292$$
$$x_{7} = -21965.9585469319$$
$$x_{8} = 25488.4558880833$$
$$x_{9} = 21249.3803723555$$
$$x_{10} = -33834.5693054934$$
$$x_{11} = -27052.737092296$$
$$x_{12} = 32270.4007511367$$
$$x_{13} = -32986.8627220526$$
$$x_{14} = -27900.492652453$$
$$x_{15} = -19422.3428903681$$
$$x_{16} = 33118.1118739225$$
$$x_{17} = 34813.5185064768$$
$$x_{18} = -16030.4592776001$$
$$x_{19} = -34682.2708868702$$
$$x_{20} = 30574.9607286225$$
$$x_{21} = 38204.2790179564$$
$$x_{22} = 18705.7058128052$$
$$x_{23} = -24509.4076256731$$
$$x_{24} = 42442.6524721704$$
$$x_{25} = -32139.1507408333$$
$$x_{26} = -18574.4221668727$$
$$x_{27} = 20401.5127178497$$
$$x_{28} = 41594.9835238138$$
$$x_{29} = 13617.3916429577$$
$$x_{30} = -41463.7402721613$$
$$x_{31} = 39899.6373793217$$
$$x_{32} = -20270.2371532321$$
$$x_{33} = 14465.575228032$$
$$x_{34} = -17726.4711883433$$
$$x_{35} = 0$$
$$x_{36} = 26336.230277608$$
$$x_{37} = -35529.96782414$$
$$x_{38} = -37225.3490351873$$
$$x_{39} = 11920.7774961659$$
$$x_{40} = -31291.43292325$$
$$x_{41} = -26204.9717446159$$
$$x_{42} = -39768.3932412975$$
$$x_{43} = 22097.2278225587$$
$$x_{44} = 40747.3118833833$$
$$x_{45} = 33965.8176625065$$
$$x_{46} = -21118.1081408212$$
$$x_{47} = 22945.0573071609$$
$$x_{48} = -38073.0338727658$$
$$x_{49} = 35661.2147583842$$
$$x_{50} = 12769.1311938499$$
$$x_{51} = -42311.4096243535$$
$$x_{52} = 37356.5947362375$$
$$x_{53} = -16878.4853984547$$
$$x_{54} = 17857.7597678008$$
$$x_{55} = 19553.622232257$$
$$x_{56} = -23661.6064602865$$
$$x_{57} = 16161.7601634659$$
$$x_{58} = -28748.239290691$$
$$x_{59} = 36508.9067380414$$
$$x_{60} = -36377.6604419003$$
$$x_{61} = -40616.0682023929$$
$$x_{62} = 29727.2308152591$$
$$x_{63} = -14334.2574401388$$
$$x_{64} = -13486.0629303382$$
$$x_{65} = -22813.7906651013$$
$$x_{66} = 28031.748190538$$
$$x_{67} = -30443.7087818787$$
$$x_{68} = -38920.7151999899$$
$$x_{69} = -15182.3860741083$$
$$x_{70} = -11789.4194932989$$
$$x_{71} = 17009.7796699387$$
$$x_{72} = 24640.6697943983$$
$$x_{73} = 28879.4935255786$$
$$x_{74} = 23792.8707458989$$
$$x_{75} = 15313.6947073257$$
so we need to solve the equation:
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The points of intersection with the axis X:
Analytical solution
$$x_{1} = 0$$
Numerical solution
$$x_{1} = -12637.7892988554$$
$$x_{2} = -29595.9777734643$$
$$x_{3} = 27183.9940576599$$
$$x_{4} = -25357.1956280906$$
$$x_{5} = 39051.9598251782$$
$$x_{6} = 31422.6838625292$$
$$x_{7} = -21965.9585469319$$
$$x_{8} = 25488.4558880833$$
$$x_{9} = 21249.3803723555$$
$$x_{10} = -33834.5693054934$$
$$x_{11} = -27052.737092296$$
$$x_{12} = 32270.4007511367$$
$$x_{13} = -32986.8627220526$$
$$x_{14} = -27900.492652453$$
$$x_{15} = -19422.3428903681$$
$$x_{16} = 33118.1118739225$$
$$x_{17} = 34813.5185064768$$
$$x_{18} = -16030.4592776001$$
$$x_{19} = -34682.2708868702$$
$$x_{20} = 30574.9607286225$$
$$x_{21} = 38204.2790179564$$
$$x_{22} = 18705.7058128052$$
$$x_{23} = -24509.4076256731$$
$$x_{24} = 42442.6524721704$$
$$x_{25} = -32139.1507408333$$
$$x_{26} = -18574.4221668727$$
$$x_{27} = 20401.5127178497$$
$$x_{28} = 41594.9835238138$$
$$x_{29} = 13617.3916429577$$
$$x_{30} = -41463.7402721613$$
$$x_{31} = 39899.6373793217$$
$$x_{32} = -20270.2371532321$$
$$x_{33} = 14465.575228032$$
$$x_{34} = -17726.4711883433$$
$$x_{35} = 0$$
$$x_{36} = 26336.230277608$$
$$x_{37} = -35529.96782414$$
$$x_{38} = -37225.3490351873$$
$$x_{39} = 11920.7774961659$$
$$x_{40} = -31291.43292325$$
$$x_{41} = -26204.9717446159$$
$$x_{42} = -39768.3932412975$$
$$x_{43} = 22097.2278225587$$
$$x_{44} = 40747.3118833833$$
$$x_{45} = 33965.8176625065$$
$$x_{46} = -21118.1081408212$$
$$x_{47} = 22945.0573071609$$
$$x_{48} = -38073.0338727658$$
$$x_{49} = 35661.2147583842$$
$$x_{50} = 12769.1311938499$$
$$x_{51} = -42311.4096243535$$
$$x_{52} = 37356.5947362375$$
$$x_{53} = -16878.4853984547$$
$$x_{54} = 17857.7597678008$$
$$x_{55} = 19553.622232257$$
$$x_{56} = -23661.6064602865$$
$$x_{57} = 16161.7601634659$$
$$x_{58} = -28748.239290691$$
$$x_{59} = 36508.9067380414$$
$$x_{60} = -36377.6604419003$$
$$x_{61} = -40616.0682023929$$
$$x_{62} = 29727.2308152591$$
$$x_{63} = -14334.2574401388$$
$$x_{64} = -13486.0629303382$$
$$x_{65} = -22813.7906651013$$
$$x_{66} = 28031.748190538$$
$$x_{67} = -30443.7087818787$$
$$x_{68} = -38920.7151999899$$
$$x_{69} = -15182.3860741083$$
$$x_{70} = -11789.4194932989$$
$$x_{71} = 17009.7796699387$$
$$x_{72} = 24640.6697943983$$
$$x_{73} = 28879.4935255786$$
$$x_{74} = 23792.8707458989$$
$$x_{75} = 15313.6947073257$$
Extrema of the function
In order to find the extrema, we need to solve the equation
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{8 x^{2}}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}} - \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the derivative equals zero),
and the roots of this equation are the extrema of this function:
$$\frac{d}{d x} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the first derivative
$$\frac{8 x^{2}}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}} - \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
Solutions are not found,
function may have no extrema
Inflection points
Let's find the inflection points, we'll need to solve the equation for this
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 0$$
You also need to calculate the limits of y '' for arguments seeking to indeterminate points of a function:
Points where there is an indetermination:
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
$$\lim_{x \to -1^-}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
$$\lim_{x \to -1^+}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
- limits are equal, then skip the corresponding point
$$\lim_{x \to 1^-}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = -\infty$$
Let's take the limit
$$\lim_{x \to 1^+}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = -\infty$$
Let's take the limit
- limits are equal, then skip the corresponding point
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, 0\right]$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left[0, \infty\right)$$
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = 0$$
(the second derivative equals zero),
the roots of this equation will be the inflection points for the specified function graph:
$$\frac{d^{2}}{d x^{2}} f{\left(x \right)} = $$
the second derivative
$$\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}} = 0$$
Solve this equation
The roots of this equation
$$x_{1} = 0$$
You also need to calculate the limits of y '' for arguments seeking to indeterminate points of a function:
Points where there is an indetermination:
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
$$\lim_{x \to -1^-}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
$$\lim_{x \to -1^+}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = \infty$$
Let's take the limit
- limits are equal, then skip the corresponding point
$$\lim_{x \to 1^-}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = -\infty$$
Let's take the limit
$$\lim_{x \to 1^+}\left(\frac{8 x \left(- \frac{6 x^{2}}{x^{2} - 1} + 3\right)}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{3}}\right) = -\infty$$
Let's take the limit
- limits are equal, then skip the corresponding point
Сonvexity and concavity intervals:
Let’s find the intervals where the function is convex or concave, for this look at the behaviour of the function at the inflection points:
Concave at the intervals
$$\left(-\infty, 0\right]$$
Convex at the intervals
$$\left[0, \infty\right)$$
Vertical asymptotes
Have:
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
$$x_{1} = -1$$
$$x_{2} = 1$$
Horizontal asymptotes
Let’s find horizontal asymptotes with help of the limits of this function at x->+oo and x->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = 0$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the right:
$$y = 0$$
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the left:
$$y = 0$$
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
equation of the horizontal asymptote on the right:
$$y = 0$$
Inclined asymptotes
Inclined asymptote can be found by calculating the limit of -2*x/((x^2 - 1*1)^2), divided by x at x->+oo and x ->-oo
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(- \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the right
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(- \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the left
$$\lim_{x \to -\infty}\left(- \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the right
$$\lim_{x \to \infty}\left(- \frac{2}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}\right) = 0$$
Let's take the limit
so,
inclined coincides with the horizontal asymptote on the left
Even and odd functions
Let's check, whether the function even or odd by using relations f = f(-x) и f = -f(-x).
So, check:
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}$$
- No
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = - \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd
So, check:
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}$$
- No
$$- \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}} = - \frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2} - 1\right)^{2}}$$
- No
so, the function
not is
neither even, nor odd
The graph


![The graph y = f(x) = -2x/(x²-1)² (minus 2x divide by (x squared minus 1) squared) - plot the function graph and draw it. Curve sketching this function. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] -2x/(x^2-1)^2](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/xy/d/92/a5cdb783ecc0497c2d19666524823.png)
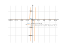 -2x/(x^2-1)^2
-2x/(x^2-1)^2