(a+3)x=(a+3)(a-2) equation
The teacher will be very surprised to see your correct solution 😉
The solution
Detail solution
Given the linear equation:
Expand brackets in the left part
Expand brackets in the right part
Looking for similar summands in the left part:
Looking for similar summands in the right part:
Divide both parts of the equation by 3 + a
We get the answer: x = -2 + a
(a+3)*x = (a+3)*(a-2)
Expand brackets in the left part
a+3x = (a+3)*(a-2)
Expand brackets in the right part
a+3x = a+3a-2
Looking for similar summands in the left part:
x*(3 + a) = a+3a-2
Looking for similar summands in the right part:
x*(3 + a) = (-2 + a)*(3 + a)
Divide both parts of the equation by 3 + a
x = (-2 + a)*(3 + a) / (3 + a)
We get the answer: x = -2 + a
The solution of the parametric equation
Given the equation with a parameter:
Коэффициент при x равен
then possible cases for a :
Consider all cases in more detail:
With
the equation
its solution
With
the equation
its solution
any x
Коэффициент при x равен
then possible cases for a :
Consider all cases in more detail:
With
the equation
its solution
With
the equation
its solution
any x
The graph
Sum and product of roots
[src]
sum
-2 + I*im(a) + re(a)
=
-2 + I*im(a) + re(a)
product
-2 + I*im(a) + re(a)
=
-2 + I*im(a) + re(a)
-2 + i*im(a) + re(a)

 Equation 2x^2+4x-4=x^2+5x+(-3+x^2)
Equation 2x^2+4x-4=x^2+5x+(-3+x^2)
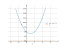 Equation k^2-2*k+5=0
Equation k^2-2*k+5=0
 Equation 5x(x-4)-x(3+5x)=4
Equation 5x(x-4)-x(3+5x)=4
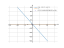 Equation (2x-1)^2-4x^2=0
Equation (2x-1)^2-4x^2=0