Integral of x²/(x²+1)² dx
The solution
1 / | | 2 | x | --------- dx | 2 | / 2 \ | \x + 1/ | / 0
-
There are multiple ways to do this integral.
Method #1
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of is .
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
TrigSubstitutionRule(theta=_theta, func=tan(_theta), rewritten=cos(_theta)**2, substep=RewriteRule(rewritten=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, substep=AddRule(substeps=[ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(2*_theta), substep=URule(u_var=_u, u_func=2*_theta, constant=1/2, substep=ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(_u), substep=TrigRule(func='cos', arg=_u, context=cos(_u), symbol=_u), context=cos(_u)/2, symbol=_u), context=cos(2*_theta), symbol=_theta), context=cos(2*_theta)/2, symbol=_theta), ConstantRule(constant=1/2, context=1/2, symbol=_theta)], context=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, symbol=_theta), context=cos(_theta)**2, symbol=_theta), restriction=True, context=(x**2 + 1)**(-2), symbol=x)
So, the result is:
The result is:
-
Method #2
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of is .
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
TrigSubstitutionRule(theta=_theta, func=tan(_theta), rewritten=cos(_theta)**2, substep=RewriteRule(rewritten=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, substep=AddRule(substeps=[ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(2*_theta), substep=URule(u_var=_u, u_func=2*_theta, constant=1/2, substep=ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(_u), substep=TrigRule(func='cos', arg=_u, context=cos(_u), symbol=_u), context=cos(_u)/2, symbol=_u), context=cos(2*_theta), symbol=_theta), context=cos(2*_theta)/2, symbol=_theta), ConstantRule(constant=1/2, context=1/2, symbol=_theta)], context=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, symbol=_theta), context=cos(_theta)**2, symbol=_theta), restriction=True, context=(x**2 + 1)**(-2), symbol=x)
So, the result is:
The result is:
-
Method #3
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of is .
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
TrigSubstitutionRule(theta=_theta, func=tan(_theta), rewritten=cos(_theta)**2, substep=RewriteRule(rewritten=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, substep=AddRule(substeps=[ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(2*_theta), substep=URule(u_var=_u, u_func=2*_theta, constant=1/2, substep=ConstantTimesRule(constant=1/2, other=cos(_u), substep=TrigRule(func='cos', arg=_u, context=cos(_u), symbol=_u), context=cos(_u)/2, symbol=_u), context=cos(2*_theta), symbol=_theta), context=cos(2*_theta)/2, symbol=_theta), ConstantRule(constant=1/2, context=1/2, symbol=_theta)], context=cos(2*_theta)/2 + 1/2, symbol=_theta), context=cos(_theta)**2, symbol=_theta), restriction=True, context=(x**2 + 1)**(-2), symbol=x)
So, the result is:
The result is:
-
-
-
Now simplify:
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
/ | | 2 | x atan(x) x | --------- dx = C + ------- - ---------- | 2 2 / 2\ | / 2 \ 2*\1 + x / | \x + 1/ | /
1 pi - - + -- 4 8
=
1 pi - - + -- 4 8
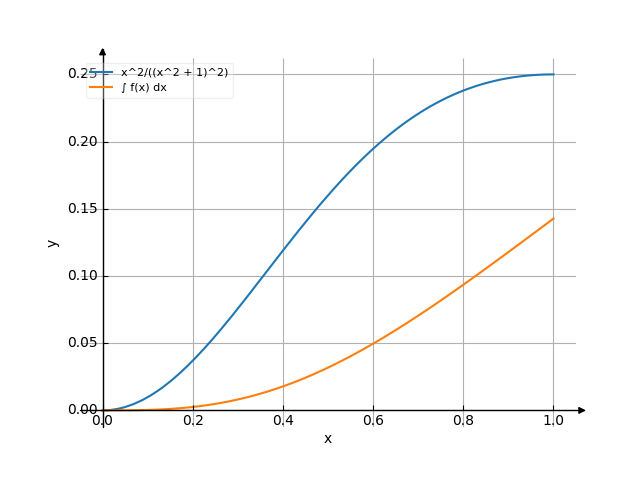
Use the examples entering the upper and lower limits of integration.

![Find the integral of y = f(x) = x²/(x²+1)² dx (x² divide by (x² plus 1)²) - with detailed solution [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] x²/(x²+1)²](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/indefinite/5/81/960a3d159960c66050af73c5a4bd3.png)
 Integral of x²/(x²+1)²
Integral of x²/(x²+1)²
 Integral of sinx²
Integral of sinx²
 Integral of xe^(6x)
Integral of xe^(6x)
 Integral of x½
Integral of x½