Integral of sin^6xcos^4x dx
The solution
1 / | | 6 4 | sin (x)*cos (x) dx | / 0
Integral(sin(x)^6*cos(x)^4, (x, 0, 1))
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
There are multiple ways to do this integral.
Method #1
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of is when :
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of is when :
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
The result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
There are multiple ways to do this integral.
Method #1
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
Method #2
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of is when :
So, the result is:
-
The result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
Method #2
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of is when :
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of is when :
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
The result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of is when :
So, the result is:
-
The result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Rewrite the integrand:
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
So, the result is:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
Let .
Then let and substitute :
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of cosine is sine:
So, the result is:
-
Now substitute back in:
-
So, the result is:
-
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
The result is:
-
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
/ | 5 | 6 4 sin(4*x) sin (2*x) sin(8*x) 3*x | sin (x)*cos (x) dx = C - -------- - --------- + -------- + --- | 256 320 2048 256 /
9 3 5 7 3 3*cos(1)*sin(1) sin (1)*cos(1) sin (1)*cos(1) sin (1)*cos(1) 11*sin (1)*cos(1) --- - --------------- - -------------- - -------------- - -------------- + ----------------- 256 256 10 128 160 80
=
9 3 5 7 3 3*cos(1)*sin(1) sin (1)*cos(1) sin (1)*cos(1) sin (1)*cos(1) 11*sin (1)*cos(1) --- - --------------- - -------------- - -------------- - -------------- + ----------------- 256 256 10 128 160 80
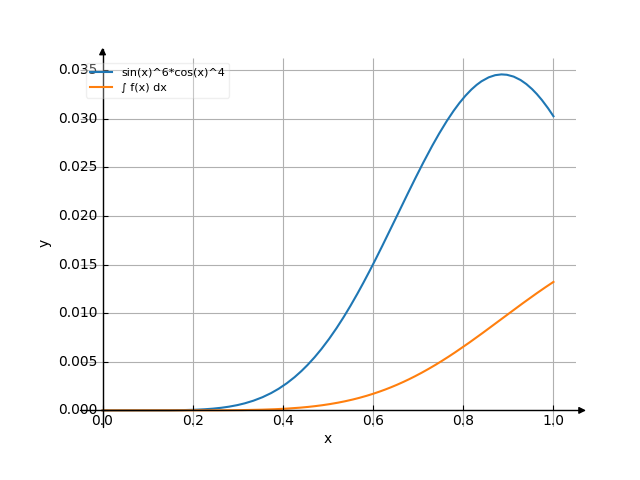
Use the examples entering the upper and lower limits of integration.

![Find the integral of y = f(x) = sin⁶xcos⁴x dx (sinus of to the power of 6x co sinus of e of to the power of 4x) - with detailed solution [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] sin^6xcos^4x](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/indefinite/6/96/faa561ee509fdef1f6ad6e6cab57a.png)
 Integral of sin^6xcos^4x
Integral of sin^6xcos^4x
 Integral of x^2e^2
Integral of x^2e^2
 Integral of tg5x
Integral of tg5x