Integral of -x^2+1 dx
The solution
Detail solution
-
Integrate term-by-term:
-
The integral of a constant is the constant times the variable of integration:
-
The integral of a constant times a function is the constant times the integral of the function:
-
The integral of is when :
So, the result is:
-
The result is:
-
-
Add the constant of integration:
The answer is:
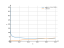
The graph

Use the examples entering the upper and lower limits of integration.

![Find the integral of y = f(x) = -x²+1 dx (minus x squared plus 1) - with detailed solution [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] -x^2+1](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/8/e8/e0f52fed1dba560b949a6b3710378.png)
 Integral of sin(5x)
Integral of sin(5x)
 Integral of (1+4x^2)^(1/2)
Integral of (1+4x^2)^(1/2)
 Integral of x/(3x²-1)^4
Integral of x/(3x²-1)^4
 Integral of x^(1/2)+2/x^(1/3)
Integral of x^(1/2)+2/x^(1/3)