sin(x/2)<-(sqrt3/2) inequation
The solution
You have entered
[src]
___ /x\ -\/ 3 sin|-| < ------- \2/ 2
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
sin(x/2) < -1*sqrt(3)/2
Detail solution
Given the inequality:
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
Solve:
Given the equation
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
- this is the simplest trigonometric equation
This equation is transformed to
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n + \operatorname{asin}{\left(- \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}$$
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n - \operatorname{asin}{\left(- \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)} + \pi$$
Or
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n - \frac{\pi}{3}$$
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n + \frac{4 \pi}{3}$$
, where n - is a integer
Divide both parts of the equation by
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
This roots
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$x_{0} < x_{1}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$x_{0} = x_{1} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$\left(4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}\right) - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3} - \frac{1}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
$$\sin{\left(\frac{4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3} - \frac{1}{10}}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$x < 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$x < 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x > 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
Solve:
Given the equation
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} = - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
- this is the simplest trigonometric equation
This equation is transformed to
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n + \operatorname{asin}{\left(- \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}$$
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n - \operatorname{asin}{\left(- \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)} + \pi$$
Or
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n - \frac{\pi}{3}$$
$$\frac{x}{2} = 2 \pi n + \frac{4 \pi}{3}$$
, where n - is a integer
Divide both parts of the equation by
$$\frac{1}{2}$$
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
This roots
$$x_{1} = 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x_{2} = 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
is the points with change the sign of the inequality expression.
First define with the sign to the leftmost point:
$$x_{0} < x_{1}$$
For example, let's take the point
$$x_{0} = x_{1} - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$\left(4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}\right) - \frac{1}{10}$$
=
$$4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3} - \frac{1}{10}$$
substitute to the expression
$$\sin{\left(\frac{x}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
$$\sin{\left(\frac{4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3} - \frac{1}{10}}{2} \right)} < - \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$
___
/1 pi\ -\/ 3
-sin|-- + --| < -------
\20 3 / 2
one of the solutions of our inequality is:
$$x < 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
_____ _____
\ /
-------ο-------ο-------
x_1 x_2Other solutions will get with the changeover to the next point
etc.
The answer:
$$x < 4 \pi n - \frac{2 \pi}{3}$$
$$x > 4 \pi n + \frac{8 \pi}{3}$$
Solving inequality on a graph
Rapid solution
[src]
/8*pi 10*pi\ And|---- < x, x < -----| \ 3 3 /
$$\frac{8 \pi}{3} < x \wedge x < \frac{10 \pi}{3}$$
(8*pi/3 < x)∧(x < 10*pi/3)
Rapid solution 2
[src]
8*pi 10*pi (----, -----) 3 3
$$x\ in\ \left(\frac{8 \pi}{3}, \frac{10 \pi}{3}\right)$$
x in Interval.open(8*pi/3, 10*pi/3)
The graph


![Solve the inequality sin(x/2)<-(sqrt3/2) (sinus of (x divide by 2) less than minus (square root of 3 divide by 2)) - Specify the set of solutions of the inequality in detail step by step. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] sin(x/2)<-(sqrt3/2)](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/inequation/4/99/3b0ca21288bcce315403a70b2a840.png)
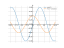 sin(x/2)
sin(x/2)
 sin(x/2)
sin(x/2)