-2sin2x>9 inequation
The solution
Detail solution
Given the inequality:
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} > 9$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} = 9$$
Solve:
Given the equation
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} = 9$$
- this is the simplest trigonometric equation
The equation is transformed to
$$\sin{\left(2 x \right)} = - \frac{9}{2}$$
As right part of the equation
modulo =
but sin
can no be more than 1 or less than -1
so the solution of the equation d'not exist.
$$x_{1} = \frac{\pi}{2} + \frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(\frac{9}{2} \right)}}{2}$$
$$x_{2} = - \frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(\frac{9}{2} \right)}}{2}$$
Exclude the complex solutions:
This equation has no roots,
this inequality is executed for any x value or has no solutions
check it
subtitute random point x, for example
$$- 2 \sin{\left(0 \cdot 2 \right)} > 9$$
so the inequality has no solutions
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} > 9$$
To solve this inequality, we must first solve the corresponding equation:
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} = 9$$
Solve:
Given the equation
$$- 2 \sin{\left(2 x \right)} = 9$$
- this is the simplest trigonometric equation
Divide both parts of the equation by -2
The equation is transformed to
$$\sin{\left(2 x \right)} = - \frac{9}{2}$$
As right part of the equation
modulo =
True
but sin
can no be more than 1 or less than -1
so the solution of the equation d'not exist.
$$x_{1} = \frac{\pi}{2} + \frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(\frac{9}{2} \right)}}{2}$$
$$x_{2} = - \frac{\operatorname{asin}{\left(\frac{9}{2} \right)}}{2}$$
Exclude the complex solutions:
This equation has no roots,
this inequality is executed for any x value or has no solutions
check it
subtitute random point x, for example
x0 = 0
$$- 2 \sin{\left(0 \cdot 2 \right)} > 9$$
0 > 9
so the inequality has no solutions
Solving inequality on a graph
Rapid solution
This inequality has no solutions

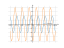 -2sin2x
-2sin2x
 -2sin2x
-2sin2x