x^2=35 equation
The teacher will be very surprised to see your correct solution 😉
The solution
Detail solution
Move right part of the equation to
left part with negative sign.
The equation is transformed from
$$x^{2} = 35$$
to
$$x^{2} - 35 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 0$$
$$c = -35$$
, then
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
or
$$x_{1} = \sqrt{35}$$
$$x_{2} = - \sqrt{35}$$
left part with negative sign.
The equation is transformed from
$$x^{2} = 35$$
to
$$x^{2} - 35 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
a*x^2 + b*x + c = 0
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 0$$
$$c = -35$$
, then
D = b^2 - 4 * a * c =
(0)^2 - 4 * (1) * (-35) = 140
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
x1 = (-b + sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
x2 = (-b - sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
or
$$x_{1} = \sqrt{35}$$
$$x_{2} = - \sqrt{35}$$
Vieta's Theorem
it is reduced quadratic equation
$$p x + q + x^{2} = 0$$
where
$$p = \frac{b}{a}$$
$$p = 0$$
$$q = \frac{c}{a}$$
$$q = -35$$
Vieta Formulas
$$x_{1} + x_{2} = - p$$
$$x_{1} x_{2} = q$$
$$x_{1} + x_{2} = 0$$
$$x_{1} x_{2} = -35$$
$$p x + q + x^{2} = 0$$
where
$$p = \frac{b}{a}$$
$$p = 0$$
$$q = \frac{c}{a}$$
$$q = -35$$
Vieta Formulas
$$x_{1} + x_{2} = - p$$
$$x_{1} x_{2} = q$$
$$x_{1} + x_{2} = 0$$
$$x_{1} x_{2} = -35$$
Rapid solution
[src]
____ x1 = -\/ 35
$$x_{1} = - \sqrt{35}$$
____ x2 = \/ 35
$$x_{2} = \sqrt{35}$$
x2 = sqrt(35)
Sum and product of roots
[src]
sum
____ ____ - \/ 35 + \/ 35
$$- \sqrt{35} + \sqrt{35}$$
=
0
$$0$$
product
____ ____ -\/ 35 *\/ 35
$$- \sqrt{35} \sqrt{35}$$
=
-35
$$-35$$
-35
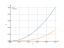
The graph


![Solve the equation x²=35 (x squared equally 35) - Find the roots of the equation in detail step by step. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] x^2=35](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/equation/8/ed/82b8e2d06501d1d79d4d429d5923b.png)
 Equation -x-2+3*(x-3)=3*(4-x)-3
Equation -x-2+3*(x-3)=3*(4-x)-3
 Equation x^2=35
Equation x^2=35
 Equation 10*(x-9)=7
Equation 10*(x-9)=7
 Equation x^2-2x+1=0
Equation x^2-2x+1=0
 x^2
x^2
 x^2
x^2
 35
35
 35
35