(x^2-1)/(x^2+1)=0 equation
The teacher will be very surprised to see your correct solution 😉
The solution
Detail solution
Given the equation:
$$\frac{x^{2} - 1}{x^{2} + 1} = 0$$
the denominator
$$x^{2} + 1$$
then
Because the right side of the equation is zero, then the solution of the equation is exists if at least one of the multipliers in the left side of the equation equal to zero.
We get the equations
$$x^{2} - 1 = 0$$
solve the resulting equation:
1.
$$x^{2} - 1 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 0$$
$$c = -1$$
, then
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
or
$$x_{1} = 1$$
Simplify
$$x_{2} = -1$$
Simplify
but
The final answer:
$$x_{1} = 1$$
$$x_{2} = -1$$
$$\frac{x^{2} - 1}{x^{2} + 1} = 0$$
the denominator
$$x^{2} + 1$$
then
x is not equal to -I
x is not equal to I
Because the right side of the equation is zero, then the solution of the equation is exists if at least one of the multipliers in the left side of the equation equal to zero.
We get the equations
$$x^{2} - 1 = 0$$
solve the resulting equation:
1.
$$x^{2} - 1 = 0$$
This equation is of the form
a*x^2 + b*x + c = 0
A quadratic equation can be solved
using the discriminant.
The roots of the quadratic equation:
$$x_{1} = \frac{\sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
$$x_{2} = \frac{- \sqrt{D} - b}{2 a}$$
where D = b^2 - 4*a*c - it is the discriminant.
Because
$$a = 1$$
$$b = 0$$
$$c = -1$$
, then
D = b^2 - 4 * a * c =
(0)^2 - 4 * (1) * (-1) = 4
Because D > 0, then the equation has two roots.
x1 = (-b + sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
x2 = (-b - sqrt(D)) / (2*a)
or
$$x_{1} = 1$$
Simplify
$$x_{2} = -1$$
Simplify
but
x is not equal to -I
x is not equal to I
The final answer:
$$x_{1} = 1$$
$$x_{2} = -1$$
Sum and product of roots
[src]
sum
0 - 1 + 1
$$\left(-1 + 0\right) + 1$$
=
0
$$0$$
product
1*-1*1
$$1 \left(-1\right) 1$$
=
-1
$$-1$$
-1
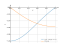
The graph


![Solve the equation (x²-1)/(x²+1)=0 ((x squared minus 1) divide by (x squared plus 1) equally 0) - Find the roots of the equation in detail step by step. [THERE'S THE ANSWER!] (x^2-1)/(x^2+1)=0](/media/krcore-image-pods/176/hash/equation/d/8e/f8a2bc0c63a1fce6f763b41a313fe.png)
 Equation (x-5)/2=2*(3x/7-1/2)/3
Equation (x-5)/2=2*(3x/7-1/2)/3
 Equation x^4-4*x^3-2*x^2+12*x+9=0
Equation x^4-4*x^3-2*x^2+12*x+9=0
 Equation sin(x)=-1
Equation sin(x)=-1
 Equation cos(x)=sqrt(3)/2
Equation cos(x)=sqrt(3)/2
 (x^2-1)/(x^2+1)
(x^2-1)/(x^2+1)
 (x^2-1)/(x^2+1)
(x^2-1)/(x^2+1)